Challenges
Profiling data, finding matching patterns or related values, and rapidly identifying the locations and lineage attributes of disparate data sources are all ways to reveal the content of data, and how it was created, deleted, or modified. Most tools available for these purposes are expensive, and designed for a specific data source (e.g., one database).
After data is discovered and transformed, application audit trails need comprehensive information about the target layouts and job runs. The details must be readily-available and secure. Logs should also track sensitive data protections and enable: user accountability, job replication, parameter modification, and issue analysis.
For example, data processing forensics may expose if a record count or value range changes beyond an established threshold; this could indicate a problem of data loss or fraud. One of the issues in student and healthcare data is the mitigation of re-ID risk and the need to measure that risk. Few data management software platforms or fit-for-purpose applications support any of these things.
Finally, in the database firewall context, you need way to log your protection policy settings and all traffic and activity into a custom, query-ready audit trail that is secure, and subject to post-deletion recovery.
Solutions
Searching & Profiling Data Sources
Using state-of-the-art database, file, and dark data discovery tools in the free IRI Workbench GUI for all IRI software, you can find the location of precise (and fuzzy matching) data patterns, and automatically discover source-specific metadata that reveals file authorship and other attributes. For example, as you locate PII values within databases, flat-files, spreadsheets, text documents, images, and other repositories, you can also automatically display the location, ownership, security, and other properties of those files.
Automated data classification for databases and files takes this one step further. This wizard allows you to define data classes and groups to which you can apply global data transformation and masking rules.
Auditing Data Masking Jobs and Scoring Re-Identification Risk
The job scripts, statistical reports, and audit logs in the IRI Voracity data management platform and its constituent IRI CoSort (SortCL) data transformation and IRI FieldShield data masking programs contain your data layout specifications, query syntax, and manipulation details. IRI is also in the process of adding task, source, and field-level policy control for IAM and lineage reporting.
An onboard re-ID risk determination wizard measures the statistical likelihood that a masked data set can still be traced to an individual based on remaining quasi-identifiers in the data set.
The XML audit log from most IRI jobs (like CoSort data transformation or FieldShield data masking) run through SortCL provide details for each input, inrec (virtual), and output definition -- including which field attributes and modification functions were specified.
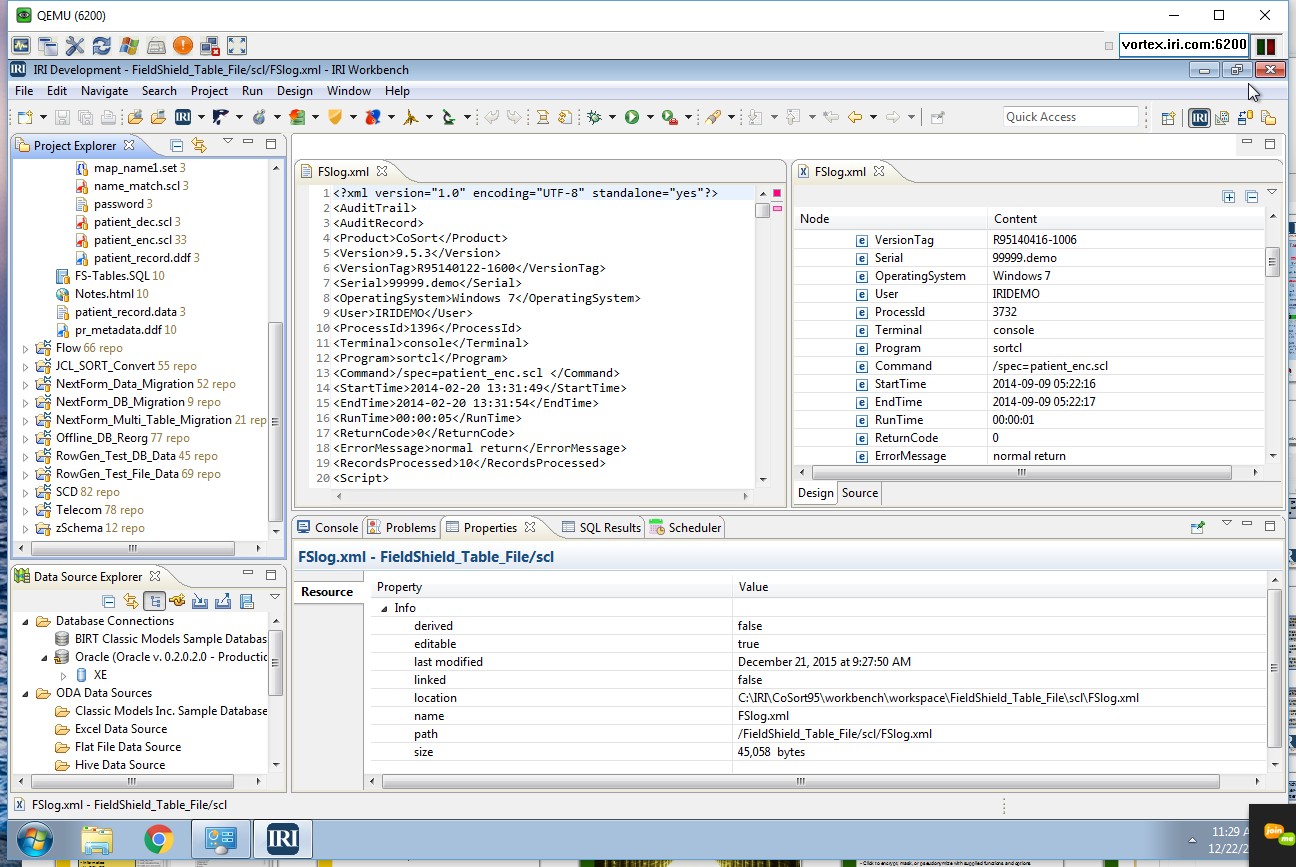
The entire job script, along with user, runtime, and environment variable information, are also recorded in the audit trail. It is easy to query and report on the logs using your preferred XML parsing tool or SortCL itself (through supplied data definition files for the logs). For example, you can query on file and field names, run dates, and job duration. You can quickly examine specific jobs without having to manually review a giant audit trail.
Phase-specific record counts -- including the number of records accepted, rejected, and processed -- plus job tuning details, are available in optional statistical log files produced with each SortCL script execution. An upcoming version of SortCL (for CoSort, FieldShield, RowGen, NextForm, and Voracity users) will feature an even more robust, granular, JSON audit log subject to authorized access. An onboard wrangling utility will assist in querying specific details from the logs and providing extracts for more visual analytics in tools like Excel and Splunk.
IRI DarkShield produces multiple audit log formats following searching and masking (or both simultaneous) operations. Text files, Eclipse-modeled tree editors, a dynamic dashboard, and feeds to the Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) SIEM environment in the cloud.

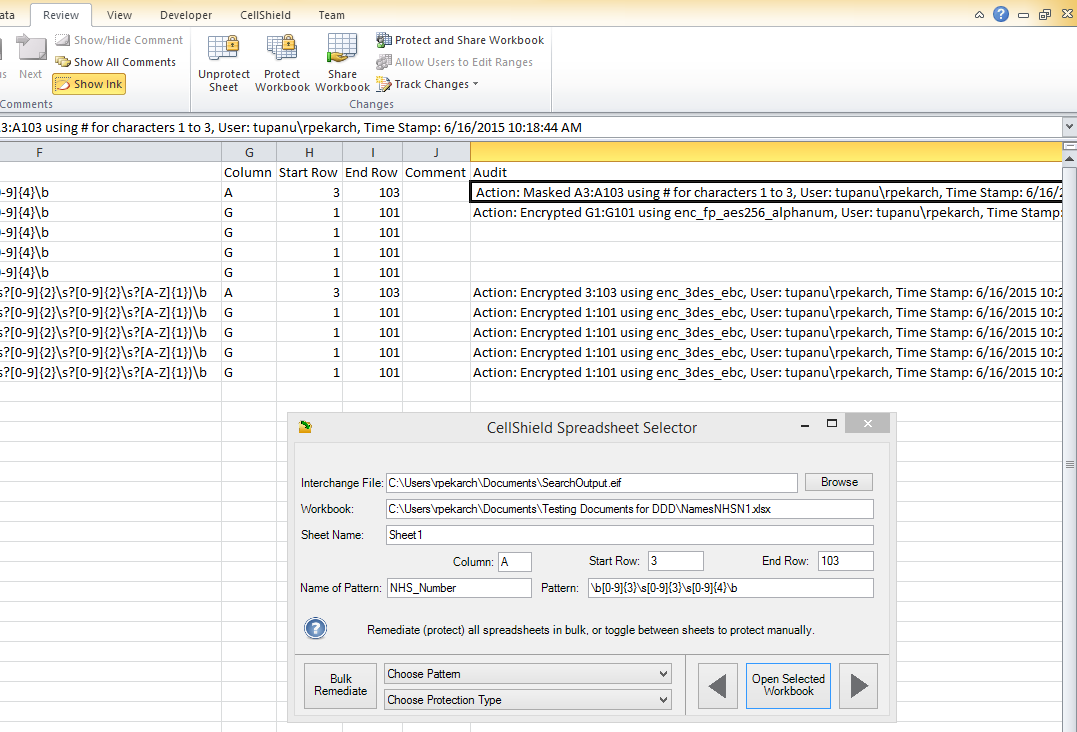
IRI CellShield EE produces an audit trail directly inside the Excel Interchange Format (.EIF) reporting file produced in a sheet after data discovery and used in conjunction with the Spreadsheet Selector dialog in Excel for remediating columns at risk.
Data and Metadata Lineage
Free data and metadata lineage capabilities are also available in the IRI Workbench, through the use of search tools and hubs like EGit for sharing and securing master data and metadata in the cloud. Graphical data lineage and metadata impact analysis for IRI Voracity ETL platform users is available through Quest (formerly AnalytiX DS and erwin) Mapping Manager, or the Data Advantage Group MetaCenter platform.
A new logging system for SortCL-compatible operations (which support CoSort, Voracity, FieldShield, NextForm, and RowGen) will produce machine-readable data for lineage analysis in fit-for-purpose platforms.
Database Activity Reporting
IRI Ripcurrent detects changes in data and schema structure in multiple relational databases where notifications can be configured. See this article for more information.


